Processes
There are three types of composite manufacturing processes: open molding, closed molding and cast polymer molding. There are a variety of processing methods within these molding categories, each with its own benefits.
OPEN MOLDING
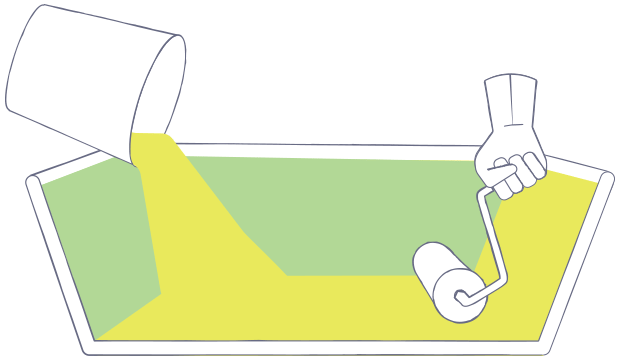
Composite materials (resin and fibers) are placed in an open mold, where they cure or harden while exposed to the air. Tooling cost for open molds is often inexpensive, making this technique well-suited for prototype and short production runs.
Closed Molding
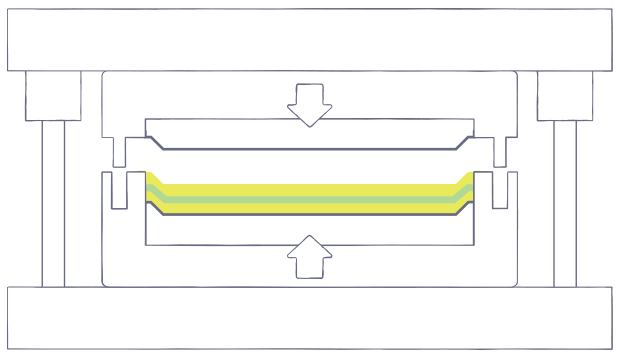
In closed-molding, raw materials (fibers and resin) cure inside a two-sided mold or within a vacuum bag (air removed) that produce huge volumes of material—up to 500,000 parts a year. Closed molding is advantageous if a two-sided finish is needed, or if high production volumes are required. Compared to open molding, closed molding processes enable manufacturers to make better parts faster, more consistently and with less waste.
Cast Polymer Molding
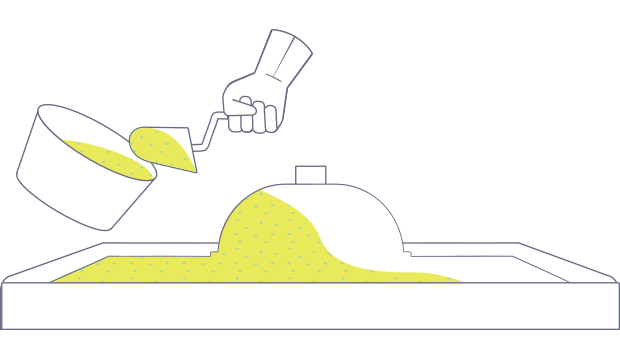
Cast Polymers refers to the production of “synthetic” cast products such as cultured granite or marble. A mixture of resin and fillers are poured into a mold, usually without reinforcements, and left to cure or harden. Cast polymer molding can be performed through open or closed molding.



